Yes,
even with different stability!
The term “half-life” is used to describe an atom or molecule that is undergoing exponential decay. It is constant over the lifetime of the decaying entity. Described differently, the term “half-life” refers to any period of time in which a a molecule or atom falls by half of its “life” even if the decay is not exponential.
Monoatomic Oxygen:
O1 is monatomic oxygen is also called “atomic oxygen” or “nascent oxygen”. It is a very powerful oxidizer. It is only found in the exosphere (aka. outer space), where radiation keeps it from bonding with anything it can come into contact with. The single atoms of monoatomic oxygen tend to quickly bond with nearby molecules. On the Earth’s surface it does not exist naturally for very long.
Dioxygen:
The common allotrope of elemental oxygen on Earth is called “dioxygen” or “diatomic oxygen”. The chemical symbol is “O2”. This is the form that is used by complex forms of life, such as animals, in cellular respiration and is the form that is a major part of the Earth’s atmosphere. This molecule is stable and has an indefinite half-life. (The natural oxygen we breathe is actually a mixture of three stable isotopes: oxygen-16 comprising 99.759 percent, oxygen-17 comprising 0.037 percent, and oxygen-18 comprising 0.204 percent. these isotopes have half-lives no longer than about 124 seconds).
Singlet Oxygen:
Singlet oxygen is (1O2). It is a highly reactive molecule that exhibits a half-life time in water of ~3.5 μs.
Singlet oxygen is the common name used for an electronically excited state of molecular oxygen (O2), which is less stable than the normal triplet oxygen (O3). Because of its unusual properties, singlet oxygen can persist for over an hour at room temperature.
Trioxygen:
Trioxygen (O3) is usually known as “ozone” or “diradical triplet oxygen” and is a very reactive allotrope of oxygen that is damaging to lung tissue. Ozone is produced when ultraviolet light or an electric spark passes through air or oxygen. It is a toxic gas that creates free radicals. The half life is approximately 30 minutes. It quickly breaks down to dioxygen (O2) and monoatomic oxygen (O1).
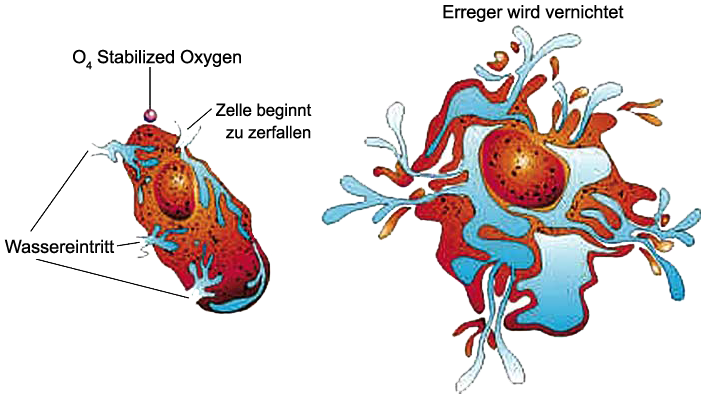
Tetraoxygen:
The existence of the metastable molecule tetraoxygen (O4) was confirmed in 2001 . It was proven in 2006 that this molecule, created by pressurizing O2 to 20 GPa, is in fact a rhombohedral O8 cluster. This cluster has the potential to be a much more powerful oxidizer than either O2 or O3.
(Metastable refers to an energy state where a molecule or atom is in equilibrium at a higher than ground state and where this state can change as it interacts with other molecules or atoms.)